Hip Dysplasia
Dogs
Hip Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a congenital disease that, in its more severe
form, can eventually cause lameness and painful arthritis of the joints.
It is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It
can be found in many animals and occasionally in humans, but is common
in many dog
breeds, particularly the larger breeds.
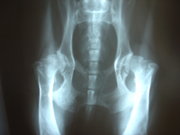 Hip dysplasia with osteoarthritis
Hip dysplasia with osteoarthritis
Description
In the normal
anatomy of the hip
joint, the thigh bone
(femur) joins the
hip in the hip joint, specifically the caput ossis femoris. The almost
spherical end
of the femur articulates with the hip bone
acetabulum,
a partly
cartilaginous mold into which the caput neatly fits. It is important that
the weight of
the body is carried
on the bony part of the acetabulum, not on the cartilage part, because otherwise
the caput can glide out of the acetabulum, which is very painful. Such a
condition also may lead to maladaptation of the respective bones and poor
articulation of the joint.
In dogs, the problem almost always appears by the time the dog is 18 months
old. The defect can be anywhere from mild to severely crippling. It can cause
severe osteoarthritis eventually.
Causes
In dogs, there is considerable evidence that genetics plays a large role in
the development of this defect. There might be several contributing genetic
factors, including a femur that does not fit correctly into the pelvic socket,
or poorly developed muscles in the pelvic area. Large and giant breeds are
susceptible to hip dysplasia, and
cocker spaniels and
Shetland sheepdogs are also known to suffer from it. Cats are also known to
have this condition, especially
Siamese.
Detection
The classic diagnostic technique is with appropriate
X-Rays and
hip scoring tests. These should be done at an appropriate age, and perhaps
repeated at adulthood - if done too young they will not show anything. Since the
condition is to a large degree inherited, the hip scores of parents should be
professionally checked before buying a pup, and the hip scores of dogs should be
checked before relying upon them for
breeding.
Prevention
Overfeeding puppies and young dogs, particularly in the giant breeds, might
aggravate the problem or bring it on earlier, because pups tend to be more
active, less aware of their physical limitations, and have immature bones and
supporting structures carrying their weight. Dogs from breeds which are known to
be prone to dysplasia, can be kept slightly leaner than normal until around 2
years old, by which time the bones are full strength and the animal can be
easily brought up to its normal adult weight. Overexercising young dogs whose
bones and muscles have not yet fully developed might also be a contributing
factor.
Symptoms
Dogs might exhibit signs of stiffness after rising from rest, reluctance to
exercise, bunny-hopping gait, lameness, pain, or wasting away of the muscle mass
in the hip area. Radiographs often confirm the presence of hip dysplasia, but
radiographic features may not be present until two years of age in some dogs.
Moreover, many affected dogs do not show clinical signs, but some dogs manifest
the problem before seven months of age, while others do not show it until well
into adulthood.
Treatment
There is no complete cure, although surgery can alleviate the clinical signs.
Depending on the extent of the problem, surgical alternatives include excision
arthroplasty, in which the head of the femur is removed and reshaped or
replaced; pelvic rotation--[triple pelvic osteotomy or pubic symphodesis]--in
which the hip socket is realigned, may be appropriate if done early enough.
Hip replacement is also possible, it is expensive but (since it completely
replaces the faulty joint) has the highest percentage of success, usually
restores complete mobility, and also completely prevents recurrence.
Since less joint mobility may result in loss of muscle mass and quality as a
dog ages, there is often an advantage in having hip replacement whilst the dog
is at an early age, while muscle is more likely to re-developed, rather than in
old age when convalsecence is longer and more difficult.
Responsible breeders who track the incidence of hip dysplasia have been able
to reduce the incidence in some breeds but not to eliminate it altogether.
References
- Ettinger, Stephen J.;Feldman, Edward C.(1995).Textbook of Veterinary
Internal Medicine(4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company.
ISBN 0-7216-6795-3
- Siegal, Mordecai (editor); UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine
Book of Dogs, 1995. Harper Collins.
ISBN 0-06-270136-3.
External links
Home | Up | Heart Valve Dysplasia | Heartworm | Hemangiosarcoma | Hemivertebrae | Hip Dysplasia | Hyperthyroidism | Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy | Hypertrophic Osteopathy
Dogs, made by MultiMedia | Free content and software
This guide is licensed under the GNU
Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia.
|