Obedience Training
Dogs
Obedience Training
Obedience training involves training an animal, most often a
dog, to obey
basic control commands such as sit, down, and heel.
There are almost as many methods of training as there are trainers, but over
time the basic strategy has shifted away from punishment or avoidance training (negative
reinforcement) to
positive reinforcement, where the dog is rewarded for doing the correct
thing during most phases of training rather than being punished for not doing
what the trainer wants.
History
Working dogs have always learned to obey commands related to the work that
they historically performed, such as when a
sheepdog
moves a flock of animals in response to a
shepherd's
whistled directions, or a hunting dog searching for (or chasing down) quarry or
leaving the treed quarry at the hunter's command.
It has been only in more modern times, as the dog has become more of a
companion than a hired servant (paid in food and a dry place to lie down) who
lived in the barn with other livestock, that obedience training has become a
separate and specific skill (for both the owner and the dog).
In the
twentieth century, formalized
dog
training originated in
military
and police
applications, and many theories on how to train a dog came out of the same
mentality that created boot camp for soldiers.
In the middle and late part of the century, however, more research into
operant conditioning and
positive reinforcement occurred as
wild animal shows became more popular-- Traditional methods of teaching
animals behavior (as with dogs) proved irrelevant when, for example, a trainer
had to instruct a
dolphin or an orca.
These aquatic mammal trainers used
clickers (a small box that makes a loud click when pushed on) to "mark"
desired behavior, giving food as a reward. The improvements in training methods
spread gradually into the world of
dog
training. Every
decade sees
new methods and new attitudes reach mainstream training classes.
Companion obedience
There are at least three levels of obedience training:
- Basic behavior
- Training for interaction with the community at large
- Competitive obedience
At a basic level, owners want dogs with whom they can pleasantly share a
house, a car, or a walk in the park. Some dogs need only a minimum amount of
training to learn to eliminate outside (be
housebroken), to sit, to lie down, or to come on command (obey a recall).
Many other dogs prove more challenging.
New dog owners might find training difficult because they expect dogs to
think and act like humans, and are surprised and baffled when the dogs don't (or
they fail to make progress because they fail to realize that the dogs don't).
Dogs who demonstrate the previously mentioned basic skills, as well as
walking reasonably well on a
leash and a few
other minor tasks, can be tested for and earn the
American Kennel Club's (AKC)
Canine Good Citizen title.
Basic behavior
The following commands are commonly taught in basic obedience classes:
- Come: This command, also referred to as the recall, is
crucial. If the dog won't come when called, it can cause great difficulty
for the handler and can place the dog in danger.
- Sit: Sitting dogs are under the handler's direct control. It is
common to precede other commands, such as the Stay command, with a
sit command. Sit and Stay are used in conjunction with many
other commands.
- Stay: This command gives peace of mind. An owner can park her dog
while doing something else.
- Lie down or down: this command allows even greater control
than sitting. Because even people without dogs are familiar with this
command and use it when dogs are bothering them, the better the dog is at
it, the better it can get along with strangers and visitors.
- Go to bed or get in: Directs the dog to go to its bed or
its
crate and to remain there until released. The dog has freedom of
movement in that location to stand up, turn around, or lie down, unlike when
placed in a Stay. Useful to keep a dog out from underfoot and safe in
a busy or complicated situation.
- Drop or drop it: Dogs pick up all sorts of things, some of
which they shouldn't have. A dog that drops anything on command, no matter
how attractive (which to a dog can be rotten and smelly), is a dog under
control that the owner can prevent from eating dangerous items or from
destroying valued personal property.
- Leave it: An adjunct to Drop, directing the dog to not
touch an item. Also useful before the dog has picked anything up. Leave
it is also used in conjunction with Take it.
- Take it: The dog leaves a desired object, such as a toy or treat,
untouched until given this command. This can protect an owner's, visitor's,
or child's fingers.
- Heel, Close, By me: The dog walks with its head
directly next to the handler's leg and does not deviate until released.
- Okay, Free, Break, or Release: Releases the
dog from Stay, Heel, Sit, and so forth. Also a general
release to play.
The specific command word is not important, although the preceding list
covers some of the more common words. Short, clear words that are easily
understood by other humans are generally recommended; that way, people will
understand what a handler is telling his dog to do and other handlers have a
good chance of controlling someone else's dog if necessary. In fact, dogs can
learn commands in any language or other communications medium, including
whistles, mouth sounds, hand gestures, and so forth.
While dogs can be trained far beyond these rudiments, a dog that obeys these
commands will be a pleasure to keep and take out. Off-leash obedience is the
hallmark of a well-trained dog.
Leash training
Leash training is another facet of training a dog which teaches them to walk
on a leash
without pulling or jerking. There are many methods for doing this, such as
simply turning and walking the other way when the dog moves in front of the
handler, or firmly grasping the leash at the collar and guiding the dog into
position beside the handler.
Today, many trainers advocate using a plain collar and leash for leash
training rather than specialized training
collars, such as
slip collars and
prong
collars. Both of these can potentially inflict damage to a dog's neck and
should not be used except in specific cases when recommended by, and supervised
by, a knowledgeable trainer. Historically, slip collars have been used as a
matter of course, and some trainers still recommend them for basic training on
any dog; such collars should be used in a way that makes a quick popping or
zipping sound to startle the dog and are then quickly released, not to choke the
dog or to put tight pressure on the dog's neck. Advocates of plain-collar
training encourage students to ask their instructors to allow them to use plain
collars, not slip collars; the techniques for training, however, are slightly
different and some instructors might not agree.
However, hard pulling even on a plain collar can damage a dog's neck, so
during times when it is not possible to work on training and the dog still pulls
on the leash, owners can use a nose
halter instead
of a collar; these are sold under brand names such as Gentle Leader and Halti.
Even these must be used carefully, not for harshly jerking a dog, as they can
jerk a dog's head suddenly to the side.
Specialized common commands
There are a few commands that many domestic dogs learn, but that are not part
of the basic repetoire.
- Stop – a dog that will simply stop whatever it is doing and lie
down on command no matter how far it is from its keeper is a dog that can be
taken anywhere. Some handlers use the
German word Platz(related to "place", i.e. stay in
position.) for this action.
- Back up – keepers of large dogs or dogs with a reputation for
aggressiveness can make strangers more comfortable by teaching the dog to
back up on command.
- Growl – the inverse of backing up. Some owners teach
non-aggressive dogs to growl on a subtle command – not the word growl,
usually a small hand gesture – as a way of letting strangers know that you
and your dog value being left alone.
- Steady – keep near by. The dog can walk free, but not dash off.
Train to this command with a long leash, calling out Steady when the
leash is taut. Continue off leash.
- Stand – dog stands still. Train from lying-down position by
lifting under belly while repeating command. Useful for grooming. Many dogs
are groomed frequently and need to stand quietly during the process.
Competitive obedience
For dog owners who enjoy competition and relish the opportunity to work as a
highly tuned team with their dogs, competitive obedience is available.
In competition, merely sitting, lying down, or walking on a leash are
insufficient. The dog and handler must perform the activities off leash and in a
highly stylized and carefully defined manner. For example, on a recall, the dog
must come directly to the handler, without sniffing or veering to one side, and
sit straight in front of the handler, not at an angle or off to one side or the
other.
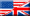
Competition obedience exercises
 This
Smooth Collie retrieves an obedience dumbbell made of wood; others are made
of metal.
This
Smooth Collie retrieves an obedience dumbbell made of wood; others are made
of metal.
A handler can choose her own commands, but the actions that the dog must
perform are well defined. As a dog progresses from novice to advanced
competition, the requirements become more challenging and the list of actions
that he must perform becomes longer. Exercises in AKC competition are offered at
three levels: Novice, Open (intermediate), and Utility (advanced); a dog must
complete the requirements at each level before moving on the next. AKC exercises
are:
- The handler leaves the dog in a sitting position at one side of the
ring, walks to the opposite side, and turns to face the dog. On the judge's
command, the handler calls or signals the dog to come. The dog must come
directly to the handler at a brisk trot or gallop, and sit squarely in
front, close enough that the handler can touch the dog's head without
bending or stretching, but not between the handler's feet. On the judge's
order, the handler commands or signals the dog to "finish". The dog must go
briskly to
heel position and sit squarely at heel.
- Drop on Recall (Open class)
- The handler leaves the dog as in the Recall exercise. On the judge's
command, the handler calls or signals the dog to come. The dog must come
directly to the handler at a brisk trot or gallop. While the dog is coming
in, the judge signals, and the handler commands or signals the dog to drop
(lie down). The dog must immediately assume a completely down position. The
dog must hold the position until commanded or signaled to come, then
complete the exercise as in the Recall.
- Following commands of the judge, the dog and handler team walks a
predetermined pattern that must include at least one left, one right, and
one about turn, as well as a fast and a slow section, and at least one halt.
During this entire exercise, the dog must maintain
heel position, and sit quickly at heel whenever the handler stops. This
exercise is performed twice in Novice class (once on lead and once
off-lead), once in Open class, and once in the Utility class, as part of the
Signal exercise.
- Sit is not an obedience exercise, but is a part of almost all of the
other exercises. The dog must sit without any command (called an automatic
sit) whenever the handler stops, and at the end of most of the exercises.
- Long Sit and Long Down (Novice and Open Classes)
- These exercises are performed by groups of dogs in the ring at the same
time. For the Novice Long Sit, the handlers command and/or signal their dogs
to sit, then to stay. The handlers walk across the ring and stand facing
their dogs. The dog must maintain the sit position without moving from its
position, barking, or whining. After one minute, the judge orders the
handlers to return, and they return to
heel position by walking around their dogs. For the Novice Long Down,
the handlers command and/or signal their dogs to down, and the dogs must
assume the down position without assistance. The handlers command and/or
signal their dogs to stay, and proceed as in the Long Sit, except that the
judge waits three minutes before ordering them to return.
- The Open Long Sit and Long Down are done in the same manner, except that
the handlers leave the ring in a single file and go completely out of the
dogs' sight. They remain out of sight for three minutes for the Sit and five
minutes for the Down.
- Retrieve on the Flat (Open class)
- The handler stands with the dog sitting in heel position facing the open
ring. On order from the judge, the handler commands and/or signals the dog
to stay, then throws an approved dumbbell at least 20 feet. On the judge's
order, the handler commands the dog to fetch. The dog must go straight to
the dumbbell at a brisk trot or gallop, retrieve it, return directly to the
handler, and sit in front as in the Novice Recall. The dog must not mouth or
play with the dumbbell. Upon order from the judge, the handler gives the
release command and takes the dumbbell. The judge then orders the handler to
have the dog finish as in the Novice Recall.
- Retrieve Over High Jump (Open class)
- This exercise is the same as the Retrieve on the flat, except that the
handler starts by standing in front of a solid jump that is as high as the
dog's shoulder height. The handler throws the dumbbell over the jump. The
dog must jump over the jump, retrieve the dumbbell, and return by jumping
over the jump again. The remainder of the exercise is the same as the
Retrieve on the Flat.
- Scent discrimination (Utility class)
- The handler presents the judge with an approved set of 5 numbered metal
and 5 numbered leather articles. The judge selects one of each, placing them
where the handler can reach them, and arranges the rest on the floor or
ground approximately 20 feet from the handler, being certain to touch each
article. At this point, the dog and handler turn so they are facing away
from the articles, and the handler uses his hands to scent one of the
selected articles. The judge takes the scented article without touching it,
and places it with the other articles. On the judge's command the handler
turns and sends the dog. The dog must go directly to the articles at a brisk
trot or gallop, select the article that was scented by the handler, and
retrieve it as in the Open Retrieve on the Flat. The exercise is then
repeated using the other selected article.
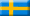
-
 An ACD finding a scent article as part of obedience competition.
An ACD finding a scent article as part of obedience competition.
For example, in the scent article exercise, the dog searches for a dumbbell
that has been scented by the handler and placed within a pile of identical metal
and leather dumbbells by an assistant. The dog must find the correct article
based only on its unique scent and retrieve it.
Dogs can earn obedience titles including an obedience championship. For
example, the
American Kennel Club (AKC) awards an "Obedience Trial Championship" (OTCh)
to the dog-and-handler team that defeats a large number of other teams in open
competition. In the
United States, a purebred dog recognized by the AKC can compete under AKC
rules; dogs not recognized by the AKC can earn titles in the
United Kennel Club (UKC),
Mixed Breed Dog Club of America (MBDCA),
American Mixed Breed Obedience Registry (AMBOR), or
Australian Shepherd Club of America (ASCA).
Contrary to what one might expect, an obedience champion might not have
excellent companion obedience skills; the actions are so highly formalized for
performance in the obedience ring that they do not automatically translate to a
dog who walks pleasantly on a leash, comes when called in the back yard, or
keeps his nose off the dinner table.
Obedience for Other Purposes
There are many reasons for training dogs beyond the level required for basic
companionship. For example,
service
dogs must obey their sit and down commands perfectly at all times, but they
do not have to conform to the rigid rules of competitive obedience.
Dogs competing in
dog sports,
such as flyball,
agility
or
Schutzhund, must be trusted in an open field, off leash and surrounded by
other people, dogs,
hamburgers,
and frisbees.
This requires more focused attention on the owner and a better recall than that
found in most household companion dogs, but again it can be a different kind of
training than that required for formal obedience.
Dog Intelligence and Training
Certain breeds, such as
Border Collies and
Golden Retrievers, are easier to train than others, such as some
hounds and
sled dogs.
Still, the Border Collie's high energy level can lead it to unwanted behavior if
its exercise and mental needs are not met, whereas the Golden Retriever can be
somewhat more relaxed.
Dog intelligence is exhibited in many different ways, and a dog who might
not be easy to train might none-the-less be quite adept at figuring out how to
open kitchen cabinets or to escape from the yard. Novice dog owners need to
consider a dog's trainability as well as its energy level, exercise
requirements, and other factors before choosing a new pet.
No breed is impossible to obedience train, but novice owners might find that
training some breeds is quite difficult. The capacity to learn basic
obedience—and even complicated behavior—is inherent in all dogs. Owners must
simply be more patient, or creative, or both, with some breeds than with others.
See also
References
External links
Sanctioning Organizations
Organizations offering obedience titles in the United States:
Home | Up | Alpha Roll | Dog Attack | Bark | Clicker | Clicker Training | Dog Collar | Animal Communication | Dog Communication | Coprophagia | Crate Training | Dog Aggression | Dog Trainer | Housebreaking | Dog Intelligence | The Intelligence of Dogs | Obedience School | Obedience Training | Operant Conditioning | Prey Drive | Socialization | Dog Society | Trophallaxis | Wardog | Dog Whistle
Dogs, made by MultiMedia | Free content and software
This guide is licensed under the GNU
Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia.
|